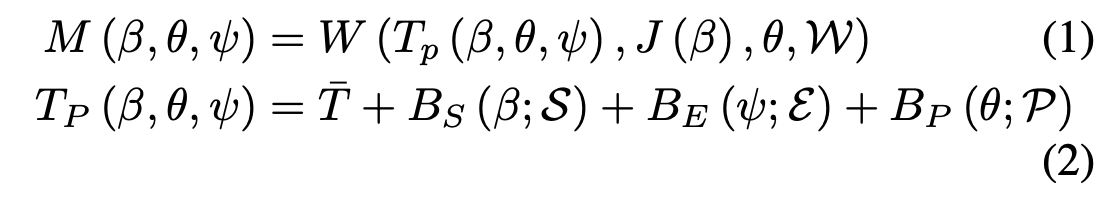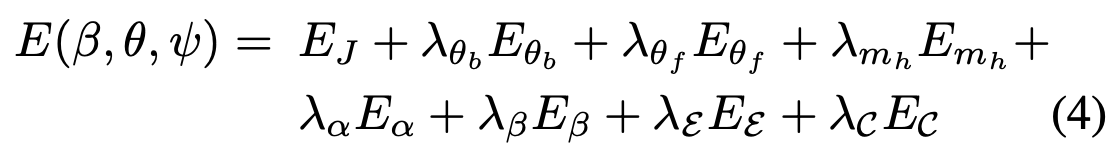[SMPLX] Expressive Body Capture: 3D Hands, Face, and Body from a Single Image¶
约 2076 个字 预计阅读时间 10 分钟
3DV Representation HMR Optimization
内容:SMPL-X 模型和 SMPLify-X 方法
挑战¶
- 想要捕获 3D 的人体、手、面信息,现在缺少 3D models 和 3D data
- 现有的方法对于 hand、facial expression 的捕获大多都与 body 隔离,少数方法通过缝合的方式整合在一起,即不是整体地去捕获
符号¶
- \(N = 10475\): verticles 数量
- \(K=54 ={24}^\text{body joints}+30^\text{finger joints}\): joints 数量,其中不算 pelvis
- \(M(\theta, \beta, \psi)\): SMPL-X model function
- \(\theta\in\R^{3(K+1)}\): pose parameters, \(K\) 是 body joints 数量,额外加上一个表示 global rotation
- 将它进一步做划分:
- \(\theta_f\): for jaw joint
- \(\theta_h\): for finger joints
- \(\theta_b\): for the remaining body joints
- \(\beta\in\R^{|\beta|}\): shape parameters (body + face + hands)
- 线性的 shape 系数,用于对 shape 正交主成分进行加权
- \(\psi\in\R^{|\psi|}\): facial expression parameters
- 线性的 facial expression 系数,用于对 shape 正交主成分进行加权
- 可以发现,面部表情不算在 pose 里,反而更像 shape
- \(\theta\in\R^{3(K+1)}\): pose parameters, \(K\) 是 body joints 数量,额外加上一个表示 global rotation
输入输出¶
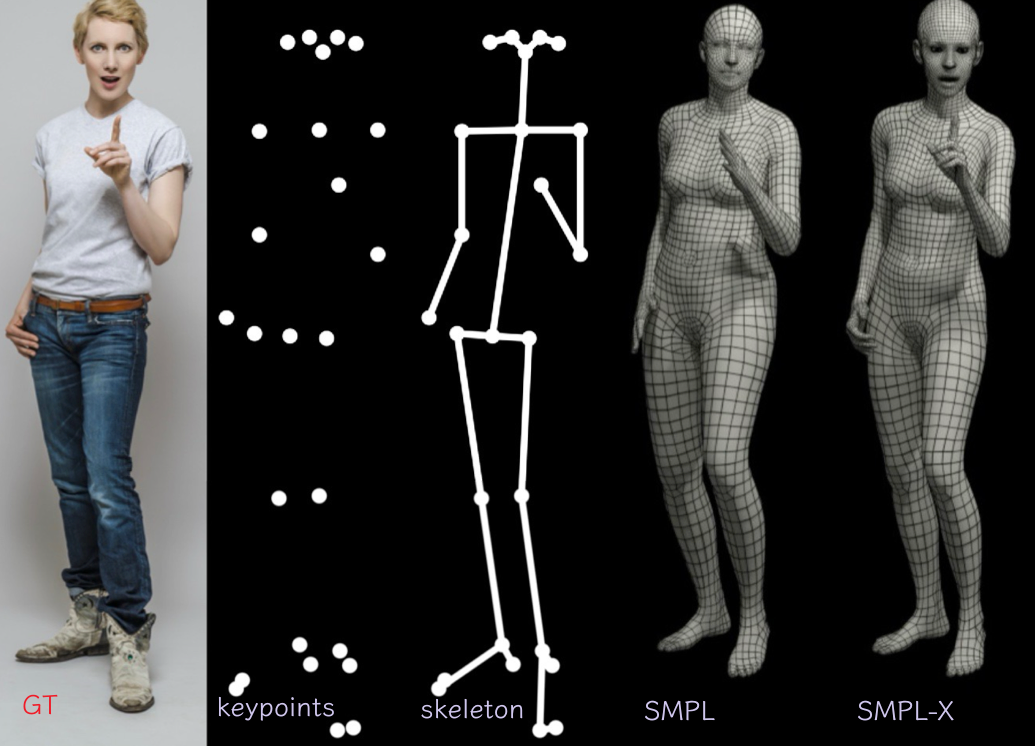
- 输入:single controlled/in-the-wild image
- 输出:3D pose & 3D shape (3D mesh & 2D joints),且包括面部和手部(SMPL-X model)
方法¶
沿袭 SMPL 的路子,首先提取 2D 的特征和信息,再通过优化来 fit 出 3D 的结果。即,改进了 SMPLify
因为如果想要用 deep learning 的方式从 single image 去 regress SMPL parameters,来获得 hands 和 face,目前不存在合适的 dataset
SMPL-X¶
增加了手部和面部内容,将 SMPL 和 FLAME head model 和 MANO hand model 结合,参数是三个部分一起训出来的。
- FLAME 除了捕捉面部和整个头部的信息,还会捕捉到脖子的一些信息(这一点对有效结合 head 和 body 至关重要)
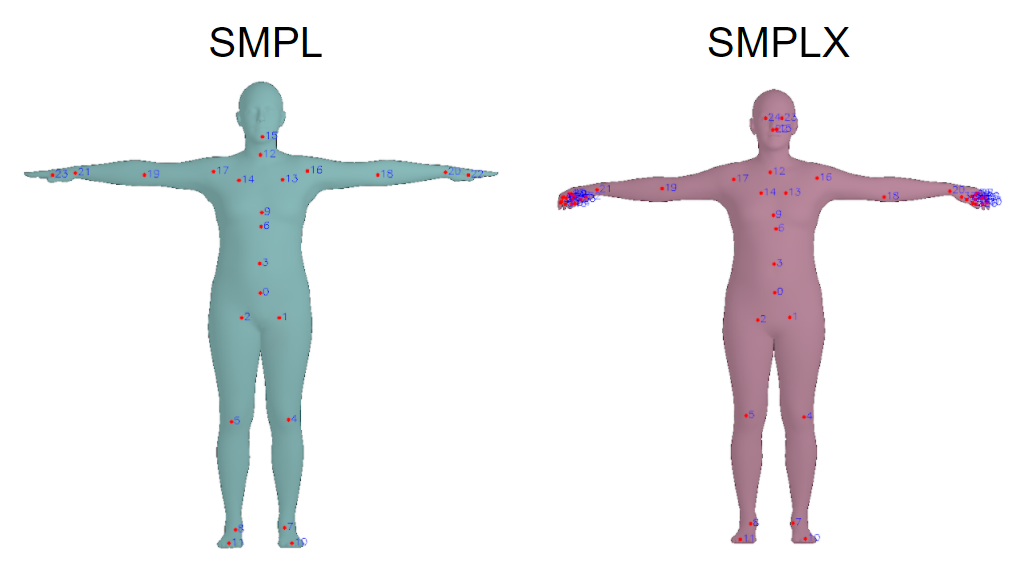
- SMPL-X 使用 standard vertex-based linear blend skinning,并且包含了 learned corrective blend shapes,一共包含 N = 10475 vertices 和 K = 54 joints(body + neck + jaw + eyeballs + fingers)
- SMPL vs SMPL-X 关于 joints 的对比
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/frankmocap/issues/91
- 这个回答里整合了一些东西:
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/579686217
-
SMPL-X 的输出可以如下建模:
- \(T_P(\beta,\theta,\psi)\): 在 T-pose 下的 blended shape
- \(\bar{T}\): template mesh in T-pose
- \(B_S(\beta;\mathcal{S}) = \sum_{n=1}^{|\beta|}\beta_n\mathcal{S}_n\): shape blend shape function
- 其中 \(\mathcal{S} = [\mathcal{S}_1,...,\mathcal{S}_{|\beta|}]\in\R^{3N\times|\beta|}\) 是每个关于每个 shape 特征的顶点的位移的正交主成分(orthonormal principle components)
- 利用 \(\beta\) 对 \(\mathcal{S}\) 进行加权得到 blend 以后的 body shape
- \(B_P(\theta;\mathcal{P}) = \sum_{n=1}^{9K}\big(R_n(\theta)-R_n(\theta^*)\big)\mathcal{P}_n: \R^{|\theta|}\rightarrow\R^{3N}\): pose dependent blend shape function
- 用来矫正由于 pose 导致的 shape 变化(例如挤肉),这里的核心思想是尽可能多的利用 rotation 信息,来更新 33K 的每个 joints 导致的对于所有节点的形体变化
- \(R(\theta): \R^{|\theta|}\rightarrow\R^{9K}\) : 9K 指的是 3*3 的 rotation matrix flatten 以后的结果,而 \(R_n\) 为第 \(n\) 个元素
- 具体转化方法使用 Rodrigues formula
- 这里做的应该就是单纯把 \(\theta\) 表示的节点旋转关系转化为 9K 的 rotation matrix,可能是考虑到一些利用冗余或来实现解偶
- \(\theta^*\) 是 T-pose,即 rest-pose 的 pose parameters,由于 \(\mathcal{P}\) 是 base T-pose 的,所以需要减去 T-pose 的 rotation
- 疑问:为什么是减法不是整个 3*3 的矩阵乘逆?是为了效率做的近似吗?
- \(\mathcal{P} = [\mathcal{P}_1,...,\mathcal{P}_{9K}] \in \R^{3N\times9K}\): 是每个关于每个 pose-dependent 特征的顶点的位移的正交主成分(orthonormal principle components)
- 两点结合来看,就是用 rotation 的细节信息来更新 T-pose 上的 vertices
- \(B_E(\psi;\mathcal{E}) = \sum_{n=1}^{|\psi|}\psi_n\mathcal{E}\): expression blend shape function
- \(\mathcal{E}\): 是 face expression 导致的特征的顶点的位移的正交主成分(orthonormal principle components)
- \(J(\beta) = \mathcal{J}\left(\bar{T}+B_S(\beta;\mathcal{S})\right)\): 3D joint locations,由于具体的 joints 位置与形状有关,所以实际上的 joints 是经过混合以后的 mesh 再 regress 出来的,而这里的 \(\mathcal{J}\) 就是一个 sparce 的 linear regressor
- \(W(\cdot)\): standard linear blend skinning function,利用 blend weights \(\mathcal{W}\in\R^{N\times K}\) 将模板 mesh \(T_p(\cdot)\) 转到估计出来的 \(J(\beta)\) 附近
- 为了 model hand,SMPL-X 做了如下设计:
- 为 fingers 分配了 30 个 joints,每个 joints 3 DoF,共 90 个 parameters
- 用 PCA pose space 来描述 MANO 的 hands pose
- \(\theta_h = \sum_{n=1}^{|m_h|}m_{h_n}\mathcal{M}\),其中 \(m_h\) 是相关的 PCA 系数,\(\mathcal{M}\) 是建模 finger pose variation 的 principle components
- SMPL-X 的总参数量为 119,其中:
- \(75 = 3 \times 25 =3 \times(24^\text{body joints} + 1^\text{global orientation})\)
- \(24^\text{lower dimensional hand pose PCA space}\)
- \(10^\text{subject shape}\)
- \(10^\text{acial expressions}\)
- \(T_P(\beta,\theta,\psi)\): 在 T-pose 下的 blended shape
SMPLify-X¶
从以下几个角度提升 SMPLify。
- 检测了面部、手部、脚部的 2D 特征,并用它们来 fit 完整的 SMPL-X 模型;
- 新的 pose prior (using VAE);
- 更快更准的穿插惩罚机制;
- 自动检测性别和适配对应的模型(原先 SMPLify 只使用 Neutral 模型)
- 用了 PyTorch,快 8x;
- 仍然是采用优化方法
- single image —[OpenPose, bottom up]→ 2D features: body, hands, feet, face
- 2D features —[SMPLify-X, top down]→ SMPL-X model
-
优化的目标函数如下:
- 其中 \(\theta_b,\theta_f,m_h\) 分别指 body 和 face 的 pose vector 以及 hands 的 PCA 系数,特别的,区别于 SMPL,这里的 \(\theta\) 都是关于 latent pose space \(Z \in \R^{32}\) 的函数
- \(E_J(\beta,\theta,K,J_{est}) = \sum\limits_{\text{joint } i} \gamma_i\omega_i\rho\biggl( \Pi_K \Bigl( R_\theta \bigl( J(\beta) \bigl)_i \Bigl)-J_{est},i\biggl)\) 是 data term
- 使用重投影误差来最小化直接估计的 2D joints \(J_{est}\) 和 3D joints 投影误差\(R_\theta(J(\beta))_i\)
- \(i\) 是 joints id
- \(R_\theta(\cdot)\) 是根据 \(\theta\),按照运动学树变换得到的
- \(\Pi_K\) 是 projection function with intrinsic camera parameters \(K\)
- \(\omega_i\) 是 confidence score
- \(\gamma_i\) 是 per-joint 的 weights(用于退火)
- \(\rho(\cdot)\) 是 robust Geman-McClure error function
- \(E_{m_h}(m_h),E_{\theta_f}(\theta_f),E_\beta(\beta),E_\mathcal{E}(\psi)\) 都是对应的 L2 priors,惩罚的是偏差
- eg. \(E_\beta(\beta) = ||\beta||^2\) 惩罚的是优化得到的 shape parameters 和训练数据得到的 “默认 shape” 的偏差
- \(E_\alpha(\theta_b) = \sum_{i\in(\text{elbows, knees})}\exp(\theta_i)\) 和 SMPLify 一致,惩罚的是肘部和膝部的不自然弯曲
- \(E_{\theta_b}(\theta_b)\) 是一个 VAE-based body pose prior
- 训了一个 body pose prior 叫 VPoser,使用了 VAE 学习了 human pose 的潜在表达,并将其正则化为一个正态分布
- 从 CMU, h36m 的 training set,和 PosePrior 数据集中恢复出 pose parameters 用来训练
- Loss:
- \(\mathcal{L}_\text{total} = c_1\mathcal{L}_{KL} + c_2 \mathcal{L}_{rec} + c_3\mathcal{L}_{orth} + c_4 \mathcal{L}_{det1} + c_5\mathcal{L}_{reg}\)
- 这两项鼓励学出正态分布:
- \(\mathcal{L}_{KL}=KL\bigl(q(Z|R)\,||\,\mathcal{N}(0, I)\bigl)\)
- \(\mathcal{L}_{rec}=|||R-\hat{R}|^2_2\)
- 这两项鼓励输出合理:
- \(\mathcal{L}_{orth}=||\hat{R}\hat{R}'-I||^2_2\)
- \(\mathcal{L}_{det1} = |\det(\hat{R})-1|\)
- 这一项用来防止 overfitting
- \(\mathcal{L}_{reg}=||\phi||^2_2\)
- 其中 \(R\in SO(3)\) 是输入的 3 * 3 的旋转矩阵,\(\hat{R}\) 是输出的 3 * 3 旋转矩阵
- \(E_\mathcal{C}(\theta_{b,h,f},\beta)\) 用来惩罚穿插
-
防止穿插的处理过程
- 使用 (Bounding Volume Hierarchies)BVH(大概就是树状结构维护几何体,然后递归地得到具体的碰撞几何体)技术检测一系列 colliding triangles \(\mathcal{C}\),并计算 local conic 3D distance fields \(\Psi\),它是由 triangles \(\mathcal{C}\) 和它们的 normals \(n\)
- 通过在 distance field 中的位置的入侵距离来惩罚
- 具体来说,例如对于两个碰撞的 triangles \(f_s\) 和 \(f_t\),入侵是双向的;并定义 \(v_t\in f_t\) 是 \(\Psi_{f_s}\) 中的 intruders,\(f_s\) 此时为 receiver,反之亦然
- 于是,\(E_\mathcal{C}\) 的具体定义就是:
$$
$$
- 为了提高速度,有许多工程上的细节 - 训了一个 Gender Classifier - 优化过程
- 类似于 SMPLify,假设我们知道 focal length of camera,首先优化未知的 camera translation 和 global body orientation
- 然后固定 camera parameters 再去优化 body shape \(\beta\) 和 body pose \(\theta\)
- 经验上发现,对 data term 里的 weights \(\gamma\) 退火有助于优化
- 优化过程中,有三个阶段:
- 首先用 high regularization 来 refine global body pose
- 慢慢增加 hand kpts 的权重来 refine 调和 pose of the arms
- 得到较好的 pose estimation 之后,再增加 hands 和 facial 的 kpts 的权重,来精细化的获得这些东西的结果
-
参考¶
最后更新:
2024年3月27日 10:01:03
创建日期: 2024年3月27日 10:01:03
创建日期: 2024年3月27日 10:01:03